Post Electrophoretic Analysis Articles
Ribonuclease Protection
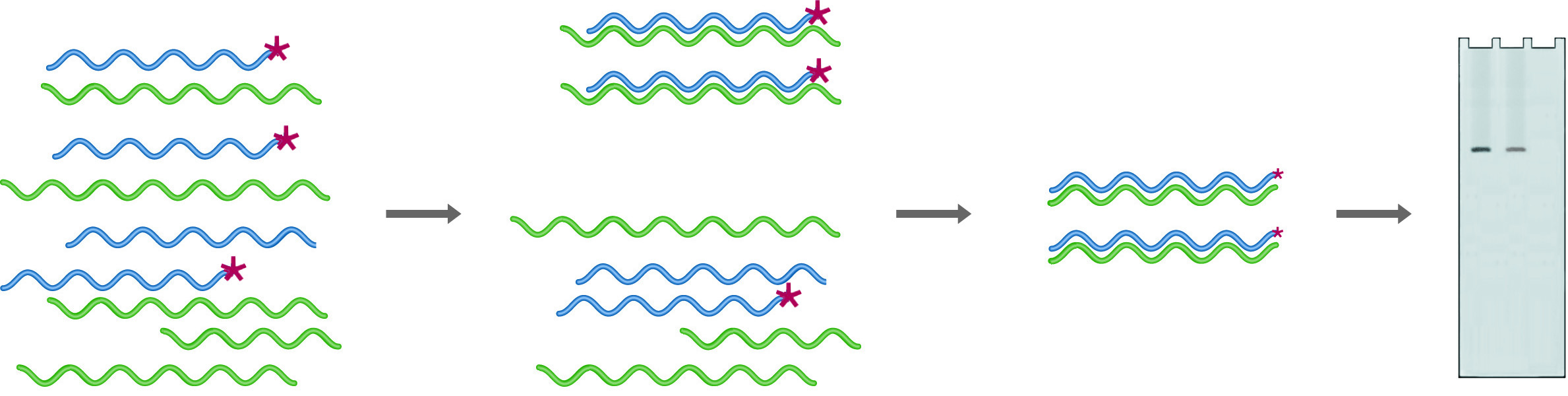
In RNase Protection, an excess of the labeled probe is hybridized into the mRNA pool. Digestion with RNase followed by gel electrophoresis (Probe + mRNA) provides quantitation of the amount of probe complementary mRNA expressed. After digestion in the absence of mRNA (Probe - mRNA) no probe remains.
Ribonuclease protection is a procedure that uses uniformly labeled RNA probes to analyze sample RNA. In this case, probes are chosen to fall entirely within the coding region, so they are only digested if no homologous RNA is present. Because the probes are uniformly labeled, the sensitivity of this technique is much higher than that for S-1 mapping. An excess of probe is mixed with the sample to be analyzed, and the hybrids are digested with RNase A, which will digest only ssRNA. The amount of probe protected from digestion (because it has hybridized with target RNA) is quantified by denaturing gel electrophoresis followed by autoradiography or by running on an automated sequencer. One of the strengths of this technique is that multiple probes can be added to a single sample, provided that they are of different sizes. A single reaction can thus give quantitative information on many different RNA species.
Ribonuclease Protection
NB: ALL REAGENTS AND GLASSWARE MUST BE RNase FREE OR DEPC TREATED.
- Probe preparation:
The RNA probe is prepared by in-vitro transcription of a cloned DNA fragment. The DNA must be cloned into a vector which provides a promoter for T-7 RNA polymerase.- To 0.5 µg of substrate in 1µl, add: 4µl of buffer, 1µl 200mM DTT, 2µl of NTP mix, 10µl 32P-CTP, 1µl (30U) placental RNase inhibitor.
- Buffer: 200mM TrisHCl (pH 8), 40mM MgCl2, 10mM spermidine, 250mM NaCl.
- NTP mix: 4mM each of ATP,GTP, and UTP in 0.5mM EDTA.
- Mix the solution well and add 10 units of RNA Polymerase (T7 or T3 ) in 1µl.
- Incubate at 37°C for 30-60 minutes.
- Add 10 units of (RNase free) DNase I. Incubate at 37°C for 15 minutes.
- Add 30µl of 1µg/µl tRNA, phenol extract and ethanol precipitate 3 times to remove unincorporated label.
- Redissolve the pellet in 100µl of hybridization solution: 80% formamide, 40mM PIPES pH 6.4, 400mM NaCl, 5mM EDTA.
- Count 1µl to confirm 109 CPM/µl.
- To 0.5 µg of substrate in 1µl, add: 4µl of buffer, 1µl 200mM DTT, 2µl of NTP mix, 10µl 32P-CTP, 1µl (30U) placental RNase inhibitor.
- Hybridize probe and sample:
Dissolve 10µg dried sample RNA in 30µl of probe solution. Mix by pipetting until all RNA is dissolved. Denature at 84°C for 5 minutes. Transfer to a bath at 35-60°C and incubate for 6-24 hours. Time and temperature must be optimized for each probe. - Digest unbound probe:Add 350µl of 20mM TrisHCl pH 7.5, 300mM NaCl, 5mM EDTA, 35µg/µl RNase A, 3µg/µl RNase T1. Incubate for 30 min. at 30°C. Add 10µl 20% SDS and 3µl 25mg/ml proteinase K to digest the RNase. Incubate at 37°C for 20 minutes.
Phenol extract and ethanol precipitate. Redissolve the pellet in 5µl and run on a denaturing PAGE gel.
NEXT TOPIC: Primer Extension
